1.What is a pneumatic valve?
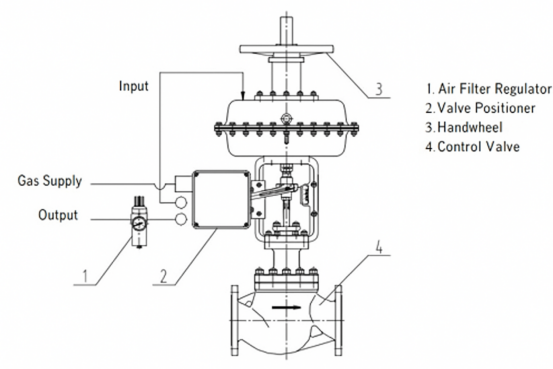
A pneumatic valve is a device that uses compressed air to actuate (open, close, or proportionally control flow through) a valve. Key components include the valve body, valve stem, trim (e.g., ball, disc, plug), seals, and a pneumatic actuator. Compressed air acts on a piston or diaphragm within the actuator, generating linear or rotary motion to position the closure element. Due to their advantages of rapid actuation, ease of automation, and reliable performance, pneumatic valves are widely used in critical industries such as chemical processing, oil & gas, power generation, and natural gas, where they play a vital role in complex process control.
2.Working Principle Analysis
Pneumatic valve operation begins at the air preparation unit (typically filters, regulators, and compressors), which intakes ambient air, removes impurities/moisture, and pressurizes it into compressed air. This air is distributed via piping to pneumatic actuators (diaphragm types for linear motion, piston types for high-force/stroke applications).
For example: When air enters a diaphragm actuator's chamber, the diaphragm elastically deforms under pressure, displacing the valve stem. The stem mechanically transfers this motion to position the trim (e.g., plug, ball, or disc), thereby opening, closing, or modulating flow through the valve body.
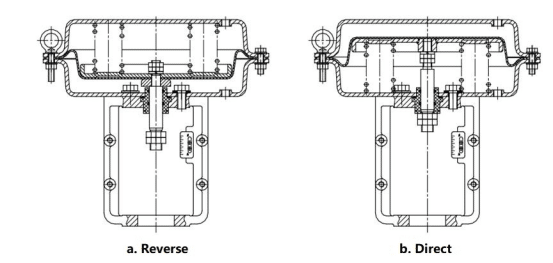
Normally Open (NO) Pneumatic Valves:
Default state: Spring force holds the closure element (e.g., plug) open, ensuring uninterrupted fluid flow.
Upon actuation: When a control signal (e.g., solenoid valve energizing) applies air pressure to the actuator, the piston/diaphragm overcomes spring force, driving the stem to move the closure element to the closed position and shut off flow.
Normally Closed (NC) Pneumatic Valves:
Default state: Spring force maintains the closure element in the closed position, blocking flow.
Upon actuation: Air pressure applied to the actuator compresses the spring, retracting the stem to open the closure element and permit flow.
The operating principle of piston pneumatic actuators similarly relies on differential air pressure across the piston. When pressurized air is applied to one side of the piston chamber, it generates linear force to drive the piston rod. This motion is mechanically transmitted through the valve stem to position the closure element (e.g., plug, ball, or disc). Piston actuators deliver higher thrust outputs than diaphragm types, making them ideal for large-bore valves and high-pressure applications where greater actuation force is required.

3.the implementation of the adjustment function
Certain pneumatic valves incorporate flow regulation capabilities beyond basic on/off control. This is achieved through specialized closure element designs like V-port balls or eccentric rotary plugs.
V-port Ball Operation:
Rotation of the ball alters the V-shaped orifice area between the ball and seat. As the ball rotates from 0° to 90°:
Opening phase: Flow area rotation angle → Flow rate increases
Closing phase: Flow area (90° - rotation angle) → Flow rate decreases
Control Mechanism:
Precise regulation requires:
Positioning system: A valve positioner converts control signals (4-20mA/pneumatic) into precise air pressure modulation
Actuator response: Modulated air pressure drives the actuator to achieve target rotation angle
Flow characterization: The V-port's engineered profile provides linear/equal-percentage flow characteristics
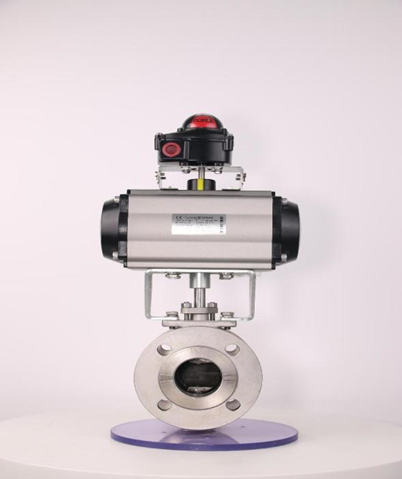


A thorough comprehension of pneumatic valves' operational principles and performance characteristics – including rapid actuation, precise flow control, and fail-safe functionality – enables engineers to:
Optimize process parameters (e.g., response time, pressure setpoints)
Enhance production efficiency through reduced cycle times
Lower operational costs via minimized energy consumption and maintenance downtime
Ensure production chain stability with reliable shutoff and leakage control meeting product standards




