Cv Calculator
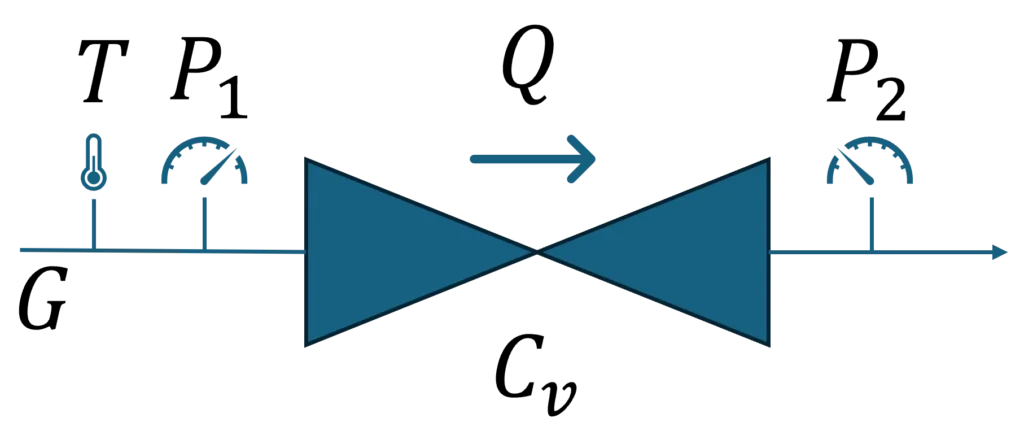
Liquid Flow Coefficient Cv Calculation
1. Variable Definitions
2. Basic Calculation Formula
Note:Applicable for incompressible liquids under non-cavitation and non-blocking conditions.
Gas Flow Coefficient Cv Calculation
1. Variable Definitions
2. Calculation Formulas by Operating Conditions
Liquid Kv Correction Calculation
1. Variable Definitions
2. Choked Pressure Drop Calculation
3. Corrected Kv Calculation
Conversion Relationship Between Cv and Kv
Note: The conversion factor 1.156 is a theoretical value derived from unit conversion relationships between US gallons and cubic meters, psi and bar.
Gas Kv Correction Calculation
1. Variable Definitions
2. Calculation Formulas by Operating Conditions
Cv and Kv Conversion Relationship
Note: The conversion factor 1.156 is a theoretical value derived from unit conversion relationships between US gallons and cubic meters, psi and bar.
V. Cv and Kv Conversion Relationship
Note: The conversion factor 1.156 is a theoretical value derived from the unit conversion relationships between US gallons and cubic meters, and between psi and bar.
